History of appearance
The first development that can be attributed to the automatic transmission class appeared in 1908 at the Ford plant in America. Model T, was equipped with a planetary, yet manual transmission. This device was not automatic, and required a certain set of skills and actions from drivers to control, but was much easier to use than the non-synchronized manual transmissions that were common at that time. The second important step in the emergence of modern automatic transmissions was the transfer of clutch control from the driver to the servo drive in the 30s of the 20th century by General Motors. Such automatic transmissions were called semi-automatic. The first truly automatic planetary gearbox "Kotal" was installed in Europe in 1930. At this time, various firms in Europe were developing clutch and brake band systems.
Drawing checkpoint "Kotal"
The first automatic transmissions were very expensive and unreliable, until experiments began in the late 30s to introduce hydraulic elements into their design to replace servos and electromechanical controls. Chrysler went this way of development, which developed the first torque converter and fluid coupling. Modern automatic transmission designs were invented in the 40–50s of the 20th century by American designers. In the 80s of the 20th century, automatic transmissions began to be equipped with computer control, for fuel economy, 4 and 5-speed automatic transmissions appeared.
Automatic transmission device
Conventionally, the entire automatic transmission can be divided into three main blocks:
- Torque converter - takes torque from the engine and transfers it further to the gearbox;
- Planetary gearbox with clutch packs and braking devices - actually regulates the gear ratio, responding to changes in speed and driving modes;
- Control unit - includes an ECU (electronic control unit) and a hydraulic unit, which directly provides a load on the friction clutches.
The main working fluid in an automatic transmission is a fluid - a special oil for an automatic transmission, it is also an ATF fluid. It is this oil that transmits the force between the transmission elements. Quite strict requirements are imposed on ATF fluid, including the intervals for checking the level and replacing.
Now consider the automatic transmission device in more detail
Automatic transmission device
- The torque converter consists of a housing filled with liquid, in which three impellers are located: a pump wheel connected to the crankshaft, a turbine wheel connected to the drive shaft of the planetary gearbox, and a reaction wheel that regulates the flow of fluid between them.
- The planetary gearbox is the main device for transmitting power from the torque converter to the wheels of the car. In fact, this is a classic planetary gear: a sun gear, satellites combined into one unit by a carrier, a ring gear. This block is also called a planetary set, and there are usually as many such planetary sets in the box as it provides for speeds. Gear shifting occurs by blocking or connecting certain gears, as a result of which the rest change direction and speed.
- Belt brake , clutch packs and pistons, overrunning clutch - these elements are needed to control the planetary gearbox, that is, blocking or connecting the necessary gears for gear shifting.
- Hydroblock - ATP liquid flow distributor. Valves create pressure to supply fluid to the desired clutch, which means to engage a certain gear.
- The control unit is an electronic "brain" that controls the valves of the hydraulic unit. It receives information about the speed and mode of movement from car sensors.
- Additional devices that are not related to the gear shift process, but are necessary for the operation of the box: automatic transmission oil pump, transmission fluid cooling radiator, filters.
Automatic transmission device and principles of operation
The main structural elements of an automatic transmission are always the same: A torque converter, which acts as a clutch. Through it, the rotational movement is transmitted to the wheels of the car. Its main task is to ensure uniform rotation without shocks. The torque converter consists of large wheels with blades immersed in torque converter oil. The transmission of torque is not carried out by a mechanical device, but by oil flows and pressure. The torque converter also houses a reactor responsible for smooth and high-quality changes in torque on the wheels of the car.
Torque converter in section
A planetary gear that contains a set of speeds. It locks some gears and unlocks others, determining the choice of gear ratio.
A set of clutches and brake mechanisms responsible for the transition between gears and gear selection. These mechanisms block and stop the elements of the planetary gear. Control devices (hydroblock) - controls the device. It consists of an electronic unit in which the box is controlled, taking into account all factors and sensors that collect information (speed, mode selection).
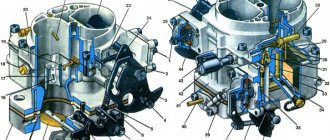
Valve body automatic transmission
Automatic box device
There are different designs of automatic transmission:
- "classic";
- variable speed stepless CVT;
- robotic mechanical DSG.
The device of an automatic "classic" gearbox can be divided into functional parts:
- The torque converter, also known as the clutch, consists of paddle wheels. The pump is connected to the engine flywheel, and the turbine is connected to the box shaft. A reactor is installed between the wheels, which turns the fluid coupling mode into a transformer. The wheels are not connected to each other, the torque is transmitted through oil pressure. The liquid absorbs vibrations and jerks from the operation of the engine and machine. The torque conversion in the torque converter has a limited interval, so a gearbox is installed in the box.
- The planetary gearbox switches speeds in the machine by changing the gear ratios on the gears. The planetary mechanism of the automatic transmission consists of central gears of different diameters - sun and crown. Satellites run between them, the axes of which are connected on the carrier. By rotating some elements and braking others, they get different speeds at the output. Couplings, brake bands and friction discs are installed to lock the gears.
- Hydraulic system. This includes an oil pump, a filter, tappets, a hydraulic distribution plate - a hydraulic block with electrovalves. ATF in the machine serves as a working fluid for transmitting engine torque, creates pressure on the clutches, and protects gearbox parts from overheating, abrasion, and corrosion. The oil pump supplies fluid to the box and maintains a constant pressure. The filter retains the wear products of the machine that come with oil. Through the channels of the valve body, the liquid enters the planetary links.
- The electronic unit contains the automatic transmission control circuit: it monitors the readings of the gearbox sensors, the position of the selector, pedals, ABS, ESP systems, etc., then issues control signals to the actuators, in accordance with the software algorithm.
Read
Do-it-yourself automatic transmission valve body repair and replacement
The device of the CVT differs from the automatic transmission in that it works without fixed speed steps. As a mechanism for changing the gear ratio, pulleys with cones on the input and output shafts are used, between which a belt is stretched. To enable reverse speed, a planetary gear is installed in the machine.
The device and principle of operation of a robotic box is more similar to a manual transmission than an automatic transmission. The DSG has two clutches and is connected to the engine through the input shaft, which the robot also has two. The input shafts are connected to the output shafts through a system of gears. To switch the speed between the gears of the secondary shafts, synchronizers are installed. The electronic unit Mechatronic controls the operation of the box.
Read
Diagnostics and repair of automatic transmission Mazda 6
How does an automatic transmission work?
When the engine is started, oil is supplied to the torque converter, the pressure begins to increase. The pump wheel begins to move, the reactor and the turbine are stationary. When you turn on the speed and supply gasoline using the accelerator, the pump wheel starts to rotate faster. Oil flows begin to start the rotation of the turbine wheel. These streams are either thrown to the stationary reactor wheel, then returned back to the turbine wheel, increasing its efficiency. The moment from the rotation is transmitted to the wheels and the car moves off. When the desired speed is reached, the pump and turbine wheels move alone quickly, while the oil flow enters the reactor from the other side (the movement occurs only in one direction) and it begins to rotate. The system goes into fluid coupling mode. If the resistance on the wheels increases (uphill), the reactor stops rotating again and enriches the pump wheel with torque. During the achievement of the required speed and torque, a gear change occurs. The electronic control unit gives a command, after which the brake band and clutches slow down the downshift, and the increasing oil pressure through the valve accelerates the upshift, due to this, switching occurs without loss of power. When the engine is stopped or the speed is reduced, the pressure in the system decreases and the reverse switching occurs. When the engine is off, the torque converter is not under pressure, so starting the engine from the “pusher” is not possible.
Automatic transmission control unit: device
The block consists of a set of spools. They control the oil flow towards the pistons (brake bands)/friction clutches. The spools are arranged in a sequence that depends on the movement of the gearbox/automatic selector (hydraulic/electronic).
Hydraulic. Applies to: oil pressure of the centrifugal governor that interacts with the output shaft of the gearbox / oil pressure that is generated during the depressing of the accelerator pedal. These processes transmit to the electronic control unit data on the angle of inclination of the gas pedal / speed of the car, followed by the switching of the spools.
Electronic. Solenoids are used to move the spools. The wire channels of the solenoids are located outside the automatic transmission housing, and go to the control unit (in some cases - to the combined control unit for the fuel injection and ignition system). The received information about the speed of the car / angle of inclination of the gas determines the further movement of the solenoids through the electronic system / the handle of the automatic transmission selector.
Sometimes the automatic transmission works even with a faulty electronic automation system. True, provided that the third gear (or all stages) is on in the manual mode of controlling the box.
Selector control
Varieties of the position of the selectors (automatic transmission lever):
- floor. The traditional location in most cars is on the central tunnel;
- stalk. This arrangement is often found in American cars (Chrysler, Dodge), as well as in Mercedes. The desired transmission mode is activated by pulling the lever towards you;
- on the center console. It is used on minivans and on some conventional cars (eg: Honda Civic VII, CR-V III), which frees up the space between the front seats;
- button. The layout has been widely used on sports cars (Ferrari, Chevrolet Corvette, Lamborghini, Jaguar and others). Although it is now being integrated into civilian vehicles (premium class).
Slots of floor selectors are:
- straight. The box lever moves along a straight path. Exceptions: the presence of a manual transmission mode;
- zigzag (stepped). The selector moves along the grooves of a complex trajectory;
- arcuate (U). Doesn't happen often. For some time it was used by the Jaguar.
Advantages and disadvantages
Compared to manual transmissions, automatic transmissions have significant advantages:
- it is easier and more comfortable to drive a car with automatic transmission, the driver does not need additional skills and reflexes, gear changes are smoother, which is especially important for moving around the city;
- the engine and leading parts of the car are protected from overloads and their resource increases;
- the resource of many automatic transmissions significantly exceeds the similar resource of manual transmissions. With timely maintenance, the need for repairs occurs less frequently.
There are no consumable parts, such as, for example, a clutch disc or a cable, and it is much more difficult to disable an automatic transmission. The resource of automatic transmissions of American and Japanese production, with modern maintenance, can reach a million kilometers. There is an opinion that cars with automatic transmission have slightly higher fuel consumption. Cars until the end of the 20th century often had incorrectly chosen moments and a limited number of speeds (2–3). On modern automatic transmissions, the number of gears is at least 4–5 (up to 19 on trucks). Modern computer automation copes with the choice of torque and speed no worse than the driver. In addition, fuel consumption on cars with manual transmission is highly dependent on the driving style and professional skills of the driver. Modern automatic transmissions have many modes, they are adapted to the driving style of the car owner.
Box-atomat in section
A serious disadvantage of automatic transmission is the impossibility of accurate and safe gear shifting in extreme conditions - when overtaking, leaving a snowdrift by quickly shifting reverse and first gear (buildup), starting the engine “from the pusher”. However, most city dwellers will choose comfortable traffic jams instead of the capabilities of a “smart” driver. The second misconception of motorists is that automatic transmissions are not designed for driving a car in racing and off-road conditions. Civilian automatic transmissions are not really designed for sporty driving and skid control - they do not have adequate cooling for such loads, and shift points are chosen for quiet driving in urban conditions. However, an automatic transmission equipped with additional cooling and reconfigured for fast gear changes will show better results than a manual transmission. Formula 1 cars are equipped with automatic transmission and handle very fast movement better than racing cars with manual transmission. Long, controlled drifts are also possible. Off-road vehicles have been equipped with automatic machines for a long time, which do not affect patency in any way. Most drivers simply don't understand how an automatic transmission works.
Formula 1 car automatic transmission
Operating modes
The automatic transmission is controlled by the driver through the selector. Each lever position is designed for specific driving conditions. The number and types of modes depend on the automatic transmission model. The decoding of the designations is indicated in the operating instructions for the car. The main modes of operation of the machine are shown in the table.
Read
Which gearbox is better automatic or mechanic: pros and cons
| Designation | Description of automatic transmission modes |
| P | Parking. An analogue of a parking brake with a shaft lock. Drive wheels are blocked. |
| R | Reverse or reverse speed. Used when stopping with the brake pedal depressed. |
| N | Neutral is used for service transportation. The shaft and wheels are not blocked, but there is no connection between the engine and the wheels. |
| D | Forward movement. |
| L | May refer to: downshift; Differential lock (cannot be turned on while driving). |
| B | |
| 2 | The speed is not higher than 2 gears. |
| 3 | The speed is not higher than 3 gears. |
| M | Manual control. Transfers are included through the signs "+" / "-". |
| S or PWR | Sport mode for dynamic driving at maximum engine speeds. |
| W | Winter is designed for winter driving. Start starts from 2nd gear. |
| OD | Overdrive is used for acceleration. |
Switching the automatic transmission to manual mode is necessary:
- when going up or down a hill;
- off-road, so as not to overheat the machine by slipping;
- for long overtaking, sharp turns and other maneuvers.
Features and capabilities
Automatic transmission allows you to better control the car, reducing the demands on the driver's action - clutch and shift knob control, makes driving less tiring. The automatic transmission has a neutral position, a parking position (the rotation of the box is additionally blocked with the help of units), a reverse gear and several speeds for movement. Switching is carried out based on the speed and conditions (for example, when driving on an incline, a reduced speed may automatically turn on). The shift time of a serviceable transmission for city cars is around 150 ms, which is much faster than the reaction of an ordinary driver. The main control of the automatic transmission is the gear shift knob, it can be located in the steering wheel area (old American and Japanese sedans or modern minivans) or at the traditional location of the automatic transmission lever. On older luxury models, the box could be controlled using a keypad. In order to avoid accidental switching or dangerous situations, various types of protection are used in automatic transmissions. In cars with automatic transmission, the engine cannot be started if the selector is in the speed position. Switching modes is carried out using the button for floor lever layouts, or pulling the lever when located on the steering wheel. The car can be removed from the parking lot only when the brake is pressed. In some cases, the slot is made in the form of steps.
Automatic transmission selector
Common modes of automatic transmission: P - parking, automatic transmission is mechanically blocked, when you are in horizontal surfaces, the use of the parking brake is optional. N - neutral. You can tow your car. L (D1, D2, S) - driving in low gear (1st gear or 2nd gear). D - automatic switching mode from the first to the last speed. R - reverse mode. In addition, the automatic transmission may have an overdrive button that prohibits shifting to a higher gear when overtaking. Neutral is usually located between D and R, or R is at the opposite end of the selector lever. This requirement was introduced to avoid accidents on the road and parking.
Also in the automatic transmission there may be various modes and protocols of operation. Eco - economical mode, implemented differently for different companies. *Snow(Winter) - Starting in second or third gear for slippery road surfaces or moving in snow or mud. *Sport(Power) - shifts gears at higher engine speeds. * ShiftLock (button or key) - unlocking the selector when the engine is off, used to transport the car if the engine or battery is out of order. Some automatic transmissions have a manual shift mode. The most successful and common version of such an automatic transmission was Tiptronic, created by Porsche. A distinctive feature is the control body, it is made in the form of the letter H and has the symbols "+" and "-".
Tiptronic Porsche Cayenne
In addition to Tiptronic, automatic transmissions include a variator and a robotic gearbox.
The device and principle of operation of the automatic transmission
The automatic transmission includes:
- hydraulic transformer;
- planetary mechanical gearbox (or shaft);
- hydraulic control system;
- electronic control system;
- differential (in front-wheel drive boxes);
- main pair (for front-wheel drive).
The torque converter is housed in a toroid-shaped housing, earning it the nickname "donut" among mechanics.
Torque converter automatic transmission
The hydraulic transformer is a mechanism with the transmission of torque by fluid flows. The device is placed between the engine flywheel and the mechanical part of the transmission. As a working fluid, oil is used, which has a low foaming ability and a viscosity that is stable from temperature and service life. The transformer acts as a clutch and changes the amount of torque taken from the flywheel of the power unit. The photo below shows the general arrangement of the box.
Schematic diagram of the automatic transmission
The structure of the torque converter includes:
- a drive wheel equipped with pump blades, which is rigidly connected to the flywheel;
- a driven wheel equipped with a turbine impeller, rigidly mounted on the input shaft of the mechanical part of the box;
- additional bladed reactor (stator);
- frame.
The design of the wheels provides for minimal gaps between the working elements; seals are additionally installed to prevent fluid from escaping. At the moment of the start of the movement, the pump vanes create a flow of oil. The resulting centrifugal force brings the oil to the outer radius of the wheel. Then the flow enters the turbine wheel, transmitting torque to the gearbox input shaft associated with it. After that, the flow is directed to the reactor, after passing through which the liquid returns to the inlet channels of the pump impeller. If the reactor is removed, the design will turn into a conventional fluid coupling, which cannot control the amount of torque.
The reactor operates in two modes - stationary and rotational. At the initial stage of the box, the reactor does not rotate, its blades are used to hold the liquid flow reflected from the turbine. When the reactor is removed, this flow will enter the pump, slowing it down and reducing transmission efficiency.
By holding the flow, the reactor increases the fluid pressure on the turbine wheel, thus regulating the torque. After alignment of the pump and turbine speeds, the reactor wheel begins to rotate. The moment the reactor begins to act is called the point of adhesion. The reactor wheel rotates at a frequency corresponding to the turbine speed.
However, the reactor does not allow the torque to be controlled over a wide range. In addition, the design of the transformer does not provide a reverse gear.
A visual representation of the principle of operation of a transformer in an automatic transmission
Planetary automatic gearbox
To expand the transformation range and ensure reverse, mechanical gearboxes are used. The most widely used are planetary mechanisms that provide a wide range of gear ratios with small overall dimensions. The gearbox consists of a central (sun) gear, around which satellites mounted on a common carrier rotate. Another gear (epicycle or crown) is installed on the peripheral part of the transmission.
The planetary gearbox in the automatic transmission is complemented by friction and brake clutches, as well as band brakes. Automatic transmissions have several planetary gearboxes that are used when switching gears. The number of gearboxes is one less than the number of speeds in the box. For example, a 4-speed gearbox is equipped with three planetary gears with different gear ratios.
The clutch consists of a set of discs and plates installed alternately. The plates are rigidly fixed on the drive shaft, and the discs are connected to the parts of the planetary gearbox. Clutch control is hydraulic. The discs are made of soft friction material, the plates are made of steel. A band brake includes a friction surface (drum) mounted on a shaft and a brake band. The tape is fixed on the box crankcase and on the hydraulic actuator.
Planetary reductor
Automatic transmission hydraulics
A hydraulic drive is used to control the speed change, which allows automating the process. In modern transmissions, hydraulics are supplemented by electronic control units that control the operation of the system.
The hydraulics of the box include:
- an oil pan equipped with a magnetic element for collecting wear products of parts;
- oil pump with centrifugal pressure regulator (spool type);
- filter for cleaning fluid from contamination;
- channels for supplying the working fluid to the actuating elements:
- valve distributors.
The oil in the box is used not only to drive the actuators, but also to lubricate and cool the components. There are two holes in the crankcase - for level control with a dipstick and a ventilation breather.
When operating an automatic transmission, it is necessary to maintain the fluid level in the sump. The resource of the box and the reliability of operation depend on this parameter.
The pressure regulator allows you to maintain the flow rate within the specified limits. Modern boxes are equipped with solenoid valves, which are controlled by an electronic unit. The block changes the flow intensity depending on the speed of the car, the throttle opening angle, resistance to movement and other parameters. Solenoid valves are used to control the flow in one or more lines, and also in gearshift drives. The valves are placed in a separate box located in close proximity to the pump. The body of the box is a so-called hydraulic plate - a part with a large number of channels for the liquid.
Hydraulic plate of automatic transmission
Hydraulic cylinders are used as actuators, converting oil pressure into mechanical work. A special case of a hydraulic cylinder is a booster used to control the operation of a disc brake or a locking mechanism.
The device of an automatic box on the example of a Toyota node is shown in a video filmed for the AvtoMaster TechCenter channel.
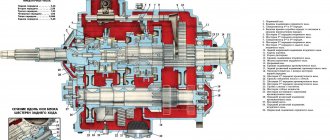
Scheme of the box
The principle of operation of the four-speed box:
- Torque is supplied to the central gear from the torque converter. At the same time, the carrier of the satellites is blocked. In any automatic transmission there are at least two planetary gears, so the rotation from the first is transferred to the second. The output shaft of the box receives torque from the second planetary gear.
- The second gear works with the help of two planetary gears. In first gear, the crown is blocked by a band brake, the carrier rotates with the satellites. From this node, the moment is supplied to the second gearbox, in which the central gear is stopped by the clutch. The output shaft of the box receives torque from the crown of the second gearbox. The gear ratio of the second gear is calculated by multiplying the gear ratios of the first and second gearboxes.
- In third gear, the ring gear and carrier of the first gearbox are stopped. Due to this, the gearbox works as a whole, without changing the speed.
- The fourth gear is overdrive. Operation is ensured by brake stop of the annulus, the torque is transmitted through the central gear.
- To turn on the reverse gear, the satellite carrier is held in the second gearbox. Torque is applied to the center gear of the second gearbox, which is then transmitted to the center gear of the first gearbox.
First gear
Second gear
third gear
fourth gear
Automatic transmission scheme
At first glance, any scheme seems complicated, but upon closer examination, everything turns out to be much simpler. In an automatic box, when blocking the elements of the planetary gear set, the necessary change in torque occurs.
The gear ratio can be more or less. With a smaller value, the sun gear must be stationary. If the value is increased, the ring gear should be locked. The carrier, which is part of the planetary gear set, changes the direction of rotation when blocked.
Automatic transmission scheme
For blocking in the design of the mechanism, special couplings are used. Their closure occurs with the help of hydraulic cylinders. Thus, gear shifting is carried out thanks to the selected algorithm for the operation of brakes and clutches.
The working fluid in the automatic transmission is distributed using a special pump. It is driven by a torque converter. The pump is the basis of the gearbox hydraulics. The principle of operation of the torque converter is a kind of conversion of torque from the engine to the box. Thanks to him, a smooth transmission is carried out.
You can also read on this topic:
Details about the engine power system
DIY chip tuning Peugeot 308
The gas distribution mechanism has a very complex design
All about car mats - TOP car mats, which are better to buy, reviews
Tuning hatchback FORD Focus 3: tricks in tuning Focus
Share on social networks
Alex SOctober 28, 2013
Published in: Useful tips and auto device
Tags: how a car works
What is an automatic transmission?
An Automatic Gearbox (AT) is a type of mechanism in a car in which gear shifting is electronically controlled.
History of appearance
The first developed model, which at that time could be attributed to automatic transmission, appeared in 1908 in America at the Ford plant. She had a planetary gearbox. Since this device was not yet automatic, it required a lot of attention from the driver, as well as a certain set of skills and actions. The good thing was that it was pretty easy to use. Then in the thirties, General Motors released a servo. The first model of the Kotal checkpoint was installed in the thirties. At the same time, friction clutches and brake bands began to be developed.
The first automatic transmission models created were very expensive and very unreliable. At the end of the 30s, experiments began to be carried out on the creation and connection of hydraulic elements in their design in order to replace servo drives and electromechanical controls. This path of development was started by Chrysler, which created the development of a torque converter. Modern automatic transmission models were created in the fifties in America. In the eighties, automatic transmissions began to be equipped with computers, in order to save fuel, five-speed automatic transmissions appeared.
Features and capabilities
Such a gearbox improves the operation of the machine control, thereby reducing the driver's actions. No need to operate the shift knob and clutch. It is equipped with a neutral position, a parking position, a reverse gear and several driving speeds. It is necessary to switch based on the speed of movement and conditions.
The speed changeover time is approximately 150 ms, which means the driver's reaction is significantly high. The main control element of the gearbox is the shift knob, which is traditionally located in the steering wheel area. In older models of cars, the box was controlled using buttons. So that it does not happen that you accidentally press the wrong place, it was equipped with several types of protection. The car can be removed from the parking lot only by pressing a button.
Here are the accepted automatic transmission modes: P - park, N - neutral gear, L (D1, D2, S) - driving in low gear, D - shift mode from first speed to last, R - reverse mode. There is also an overdrive button that prohibits the shift to the highest gear when overtaking other cars. Neutral is usually located between D and R. This requirement was made in order to avoid accidents.
Also there are a number of other modes.
- Eco is an economical mode designed for different companies.
- Snow (Winter) - movement from second or third gear.
- Sport (Power) - gears can be shifted at high engine speeds. Shift Lock - unlocking the selector when the engine is off. Some automatic transmissions have a manual gearshift mode.
The device of the automatic transmission
How does an automatic transmission work and how should an automatic transmission work? We will answer these questions in this section of the article. In order to understand how it works, we will conditionally divide it into 3 parts: hydraulic, mechanical and electronic. Mechanical is responsible for shifting gears, hydraulics creates a force of impact on the mechanics. Well, the electronic one is the brain responsible for switching modes, as well as feedback from all auto systems.
The heart of the car is the engine. The gearbox mechanism converts the power and element of the engine to drive the machine. Much of this hard work falls on the torque converter and transmissions.
The torque converter performs the clutch function. It consists of a pair of paddle machines. The turbine and the pump are closely connected, which promotes the circulation of liquids. There are no leading elements in it, since the flow of working fluids is carried out through the engine. The reactor blades have a special profile, which taper gradually. Due to this, the speed of the liquids gradually increases, and the liquid ejected in the direction of rotation drives and pushes it.
Principle of operation
The hydraulic part is an intermediary, which is the main link. The electronic part is considered the brain of the transmission. The transmission does not claim to be the main link. The main goal of the automatic transmission is considered to be the transformation of the KM motor into a force that creates conditions for the movement of the vehicle. A more complete principle of operation is described above.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pros.
- A car with an automatic transmission makes it possible to concentrate on the road without having to switch it. This is especially true for owners of cars with a manual transmission. Even in driving schools, you can be trained already on an automatic box. Only in this case you will be forbidden to drive a car with mechanics. Beginners often have problems getting off the ground, usually the car stalls.
- In vehicles equipped with an automatic transmission, this process is electronically controlled.
- Cars with automatic transmission have a smooth movement, which is achieved by a smooth change in the size of the engine element.
- In Europe, 80% of cars with automatic transmission were sold. In Russia, 48.3%.
Minuses.
- The main disadvantage of automatic transmission is the high requirements for the operational properties of service.
- The fuel consumption of such a box is 1-2 liters higher. The mechanics have no problems with this, but the machines are complex and require a lot of maintenance.
- If used incorrectly, you can easily break the automatic transmission. Moreover, the service is expensive.
- On a car with automatic transmission, towing is difficult and should not be done. Also, when the battery is discharged, it is impossible to start from the pusher.
Automatic transmission design
A standard automatic transmission consists of the following main elements:
- torque converter;
- planetary reductor;
- clutches (friction and overrunning);
- drums;
- shafts.
The design and principle of operation of the torque converter
The torque converter is installed between the gearbox and the engine. The purpose of this element is as follows - the transmission of torque when starting a car. At high speeds, this device is usually blocked by clutches located inside. Thanks to this, fuel is consumed less and slippage disappears.
The torque converter device is as follows: three wheels: turbopump, stator, turbine. Usually the stator is fixed and connected to the body of the automatic box. In some designs, the stator may not be attached, and its immobility will be ensured by special couplings. Thanks to this braking, a wide range of speeds is provided.
It is thanks to the use of a torque converter that there is no kinetic energy and, accordingly, the car moves smoothly, there is no load on the car's transmission. The only negative is slippage, as a result of which additional heat is generated, and fuel consumption increases.
The principle of operation of a torque converter is different from a hydraulic clutch. He has different moments on the turbine and pump wheels. To save fuel, a rigid attachment between the turbine and the pump began to be introduced into the device. Such braking is carried out when a higher speed is reached. When controlling the automatic transmission using a computer, the moment when blocking is necessary is selected by the control program.
Also, this blocking allows you to have the same fuel consumption as that of a manual transmission. With its help, you can implement engine braking and, as well as economical fuel consumption. In this mode, fuel injection stops, but only at the moment of blocking the elements of the torque converter.
Planetary gear and its operation
The automatic transmission has a mechanical transmission. It is necessary for the implementation of the movement of the car in reverse, which is carried out using a step change in torque. The planetary gearbox used in the design of the automatic gearbox has a compact size and coaxiality. Usually there are several of them in the automatic transmission. They are connected in series with each other. Thus, their joint work is realized.
Thanks to this design, the mechanical component of the automatic transmission provides the required number of steps. In modern car models, from 6 to 8 steps are implemented, there are also 9-speed ones. The planetary gearbox in the box is called the planetary gear set.