Brake systems KAMAZ 6520
The brake mechanisms of the drum-type system with two inner shoes, the diameter of the brake drums is 420 mm, the width of the pads is 180 mm. Front brake chambers - diaphragm, type 30, rear - type 30/24.
Drive service brake systems
— pneumatic, separate. The number of receivers is 6, with a total volume of 120 liters.
Nominal pressure in the pneumatic drive (6.5-8.0 kgf/cm2).
compressed air pressure
in the pneumatic actuator, adjust the screw 2 of the pressure regulator (see Fig. Pressure regulator). When the screw is turned in, the regulated pressure increases, when it is turned out, it decreases.
in the brake system of the car (see Fig. Pressure regulator). The dryer is made together with a pressure regulator and is designed for cooling, condensate separation and maintaining the required pressure of compressed air coming from the compressor. Compressed air supplied from the compressor to the dryer passes through the felt disc and granulate, is cleaned and enters further into the brake system. After the brake system is filled and the pressure regulator is actuated, the granulate is cleaned of moisture by air escaping into the atmosphere through the atmospheric outlet of the dryer. Maintenance of the dryer consists in the periodic replacement of the filter element as it becomes dirty (approximately once every two years).
For tire inflation
the pressure regulator has an air bleed valve closed with cap 1 (see Fig. Pressure regulator). When taking air with the tire inflation hose from the tool kit, connect it instead of the cap by screwing the wing nut all the way down and reduce the compressed air pressure in the pneumatic drive, because there is no air bleed when the compressor is idling. To reduce pressure, open the condensate drain valve on any receiver. Drain the condensate from the receivers daily at the end of work. The pressure of compressed air in the pneumatic drive must be nominal.
Open the condensate drain cocks by moving the pusher by the ring to the side (see figure). Do not pull the stem down or push it up. After draining the condensate, bring the compressed air pressure in the pneumatic actuator to the nominal value.
The control of the working
brake systems of the car is carried out by a two-section crane driven by a pedal.
Adjust the position of the brake pedal relative to the cabin floor according to the Scheme for installing the pedal on the brake valve. By adjusting the mounting and adjusting bolts, it is necessary to ensure the position of the pedal platform at an angle of 35o ± 2o and the pedal free play of 10-15 mm. Fix the adjusting bolt with a lock nut, cover the adjusting bolt with UG7 sealant before adjusting.
The design of the pneumatic drive of the brake mechanisms of the car provides for the possibility of emergency release with the horizontal position of the handle of the control valve for the parking and emergency brake systems , regardless of the degree of filling of the receivers with air. Thus, it is possible to start driving after the parking brake warning lamp goes out. It should be remembered that in the absence of air in the receivers (manometer readings), the service brake system does not work and braking must be carried out with a manual brake valve. In addition, in the absence of compressed air in the pneumatic system, the car can be released using the screws of the emergency brake release mechanism, which are built into the cylinders of the spring energy accumulators.
The vehicles are provided with the installation of adjusting levers with automatic adjustment of the gap in the brake mechanisms between the brake lining and the drum.
To ensure the normal operation of the automatic adjusting levers, as well as after changing worn brake linings, it is necessary to make an initial adjustment of the strokes of the brake chamber rods. In the future, the need for adjustment disappears until the lining is completely worn out.
Adjustment of rod strokes
brake chambers should be carried out when the brake chamber rod is in a fully disengaged state (release the energy accumulator using the parking brake control valve) and disconnected from the adjusting lever. Carry out the adjustment in the following order:
- make sure that the lever is moved by hand in the direction of braking and fully returns to its original position;
- by rotating the worm of the adjusting lever, align the holes of the lever body and the fork of the brake chamber rod. Attach the brake chamber rod with a pin, washer and cotter pin (see Fig. Adjusting the brakes with automatic levers, 1);
- press the control block of the adjusting lever all the way in the direction of its rotation according to the arrow on the housing (see Fig. Adjusting the brakes with automatic levers, 2);
- connect the fixing bracket and the lever control block with a bolt and nut, without disturbing the position of the control block;
- by rotating the worm of the adjusting lever, open the pads until they come into contact with the brake drum (see Fig. Adjusting the brakes with automatic levers, 3);
- turn the worm in the opposite direction approximately 3/4 of a turn (see Fig. Adjusting the brakes with automatic levers, 4). In this case, the characteristic operation of the gear clutch of the adjusting lever should be felt and the torque of the worm should be at least 42 N.m;
- make sure the lever works. To do this, supply compressed air 5 times at a pressure of 0.b ... 0.7 MPa (b ... 7 kg / cm2) into the brake chamber. In this case, the lever worm must turn clockwise by a certain angle (see Fig. Adjusting brakes with automatic levers, 5);
- check that when supplying and releasing compressed air, the brake chamber rod moves without binding. The stroke of the camera rod should be within 40 ... 45 mm.
With a larger stroke, adjust it by rotating the worm; - make sure that in the braked state the drum rotates evenly and freely, without touching the shoes.
Cars can be equipped with a 4-channel anti-lock braking system (ABS) of type 4S / 4M brakes (4 sensors / 4 modulators) with a microprocessor control unit from Wabco (Germany).
The main purpose of the system is to automatically maintain optimal braking of the car without blocking (skid) the wheels, regardless of whether the road is braking - slippery or dry.
Thanks to this, cars acquire a number of advantages:
- increasing active safety by providing stability and controllability during braking and increasing the braking efficiency of the car, especially on wet and slippery roads;
- tire life extension;
- the possibility of increasing the average safe speed.
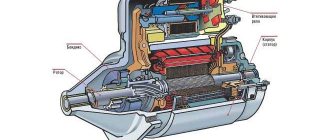
Main brake valve KAMAZ 5320: device
KamAZ, MAZ, ZIL are those cars that ordinary motorists do not care about. But, despite this fact, they all have a rather interesting design, the nuances of which are better to know, especially if you have to get to know these giants better. In particular, special attention should be paid to the brake system, in the device of which a brake valve is allocated (at the moment we mean the KamAZ car, which will be discussed later).
The device of the brake two-section crane
The main brake two-section crane KamAZ is designed to control the working brake systems of the car and the combined drive of the brake mechanisms of the trailer, which is fully consistent with the arrangement of the unit.
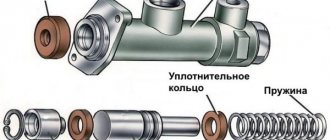
The main components include: a large piston, a follower and a small stepped piston, upper and lower valves, an elastic element, a pusher, a lever, a pin and a small piston pusher.
The first and second outlets of the valve are connected to the brake chambers of the front and rear wheels by means of intermediate pneumatic devices, while the third and fourth are connected to the receivers of separate service brake drive circuits.
Being in the initial position (with the brake pedal lowered), the valves are closed, the first output is disconnected from the fourth output, and the second output is disconnected from the third (“communication” with the atmosphere occurs through the valve).
When the driver of the vehicle starts to brake, the brake force applied to the pedal is transmitted to the stepped piston through the elastic element. Moving down, the piston closes the outlet of the valve, thereby cutting off the outlet of the brake circuit from the environment.
When the upper piston moves down, already compressed air passes into the circuit of the working brake mechanisms of the rear wheels. The action of compressed air, together with the work of the springs of the stepped upper piston, balance the force on the pedal.
Thus, the principle of operation of the KamAZ brake valve can be called a fairly simple and natural process.
Causes of crane failures
Like any other vehicle, the KamAZ car sometimes encounters operational problems, which are often caused by the brakes of the structure, or rather, the malfunctions in the assembly.
In particular, the main malfunctions of a two-section valve include the loss of tightness of the sealing rubber elements (piston and rings) and, as a result, air leakage from the system, as well as sticking of the pusher, which makes it impossible to completely disengage the machine.
As for air leakage into the atmosphere , it can occur through the inlet port (which is mainly caused by defects in valves and springs) and along the housing connector (the result of a defective sealing ring and damage to the end surfaces of the housing).
Sticking of the lever is often caused by contamination of the lever mechanism, which resulted in damage to the protective cover.
Another fairly common malfunction of the brake system of a KamAZ vehicle is a slow increase in pressure in the lower section with its growth in the upper part. This problem is caused by swelling of the O-rings.
Do not forget about the possibility of a violation of the follow-up action along the lever, the cause of which is a defect in the elastic element.
How to check the brake valve Kamaz
The main brake system valve , which belongs to a two-section type (in this case, KamAZ vehicles are meant), is located on the left side member of the frame and is attached to it using a special bracket.
Diagnosis of this mechanism should become a regular action.
, since with periodic inspection, systematic cleaning of accumulated dirt and checking the tightness of all connections, you will be guaranteed the
stable operation of the specified unit.
In particular, during visual inspection, special attention should be paid to the condition of the protective cover of the crane . This part should not have breaks and must fit snugly around the entire perimeter of the brake valve body.
The tightness of the joints can be checked using a soap emulsion in two positions of the valve - inhibited and disengaged.
If bubbles appear on the applied composition, then there is still an air leak. In the event that it exits through the atmospheric outlet of the valve of interest to us, it is necessary to check the tightness of the inlet valve and the operability of the outlet valve.
If, as a result of diagnostics, such defects are found, then such a valve must be replaced.
The brake valve drive also needs periodic inspection, cleaning and lubrication of the swivel joints.
When carrying out all diagnostic activities, do not forget about the brackets, rods and levers that connect the brake pedal to the brake valve. They should also be periodically cleaned of small foreign objects and dirt.
If
the brake pedal is loose, then be sure to adjust its stroke, which can be done using an adjusting fork, through which the length of the rod connecting the machine pedal to the first intermediate drive lever is set.
If for some reason the brake valve drive has already been disassembled before, then during assembly it is necessary to achieve complete alignment of the lower hole of the intermediate lever and the cab tipping axis. After that, by changing the length of the rod that goes from the pedal to the front lever, you should set the pedal to the desired position in the cab.
Brake valve replacement
Replacing the main brake valve KamAZ, the approximate scheme of which was given above, requires the distribution of time into two successive stages: removing the old mechanism and installing a new element.
How to remove the brake valve, sequence of actions
To remove the brake valve, you must first bleed air from the air reservoirs located in the front and rear axles. Then, you should unscrew the union fastening nuts connecting the tips of the pneumatic pipelines with the tees and the tap adapter. After that, unfasten and dismantle the pin connecting the rear link fork with the crane lever.
Unscrew the nuts of the mounting bolts holding the valve upper body plate next to the frame brackets and remove the valve itself.
Installation of a new two-section crane
After the removed part is in your hands, install a new crane on the brackets of the left side member and secure it there with bolts, nuts and spring washers. Now, you need to attach the rear traction fork to the lever, insert the finger back and cotter it . Then it remains only to bring the tips of the pneumatic pipelines to the tees and adapters of the crane by screwing and tightening the union nuts, and then start the engine and fill the pneumatic actuator of the brake systems with air.
After checking the tightness of all pipelines and the brake valve itself, you can assume that you have successfully completed the task of replacing the KamAZ brake system valve, which belongs to a two-section type on this car.
Repair of the brake valve KAMAZ
We just found out how to replace the brake valve on KamAZ, but how to disassemble it if repairs are required? In fact, there is nothing particularly complicated here, the main thing is to strictly follow the instructions.
How to disassemble the crane
First of all, if you want the air channels to remain the same when reassembling, then remember to mark all three removable parts. After marking, the sequence of further actions is as follows:
- Using the “12” wrench, we unscrew the fixing bolts that hold the body and the base plate next to each other.
- Then, assembled with a lever, we dismantle the upper part of our crane and separate it from the plate.
- We remove the upper piston, the lower part of which is the valve seat.
- At the top of the piston there is a damping device, which is designed to dampen sharp shocks from the lever. The fixing screw of this assembly, in addition to its direct purpose, performs another, no less important function - control of the lower section of the crane in case of failure of the upper one. In this case, the lower section will fully retain its performance. In the event that damper replacement is required, the previous position of the fixing screw should be retained. Also, during operation, the gap between it and the piston pusher does not change.
- At the next stage, in order to get to the valve of the upper section, you need to unscrew the four fixing screws (using a “12” wrench) and separate the housing.
- Next, we pull out a small piston from it, having previously swung the large part a little. It is he who provides the pneumatic control of the lower section.
- The top section valve is held in place with a retaining ring, after removing which you can remove the valve assembly itself.
- Do not forget about the sealing unit, which consists of a support ring and two cage seals. After removing the conical retaining spring, move the cap slightly.
- Now, if you see that the working side has become unusable, but there is nothing to replace it with, you can simply rearrange it up with the surviving part.
- To dismantle the valve of the lower section, it is enough to remove the retaining ring from the body of this section.
- Next, you should dismantle the spring clamp and the protective cover, after which, with the key to "22", unscrew the plug of the lever axis.
- By turning the nut, press out the axle, and if there is an increase in the transverse play of the lever, then be sure to replace the two polymer bushings. As for the lever roller, most often it wears out in only one place, the reason for which is the lack of lubricant on its axis.
- To carry out repair measures, the roller axis should be knocked out using a punch with a diameter of 10-12 mm. and taking out the roller, perform its processing on a lathe or grinding machine, up to the removal of wear marks.
- Next, the pusher itself is pressed out, after which it is cleaned of traces of corrosion.
- The groove of the bushing is also subject to cleaning, into which it is subsequently necessary to put new grease.
Note! In the event that, with the brake pedal depressed, you have already noticed the hiss of a crane coming through the drive lever housing, you should check the seal of the specified piston, since most likely it is not tight.
Attention! To remove the axle, use the M6 threaded hole, into which a bolt with a nut and washer is screwed.
Now it remains to replace the worn parts and assemble the mechanism in reverse order.
Assembly of a two-section brake valve KamAZ
When assembling parts, do not forget to apply grease to all mating surfaces, and when joining body sections, check the integrity of the sealing rings. A small free play of the actuator is provided by a stop screw. But all this is just a preface, since the reverse assembly scheme of the two-section KamAZ brake valve provides for the following actions:
- Using the adjusting screw in the upper piston, set the desired distance and lock the fastener.
- Then, it is necessary to reinstall the upper piston and, if necessary, press it with a transport clamp.
- We collect the device, with the installed lever and base plate.
- Next, we screw the adjusting bolt into the lever, and this must be done so that there is no gap between the roller and the pusher.
- We connect the brake valve to the compressed air system and switch the lever three times until it stops. There should be no jamming and in the normal state the switch quickly returns to its original position.
- The next step is to pressurize the outlets with air. By moving the lever three more times, the pressure in the terminals should change. The total stroke of the lever to the stop should correspond to 31.1 ... 39.1 mm, with a pusher stroke of 12.5 ... 15.7 mm.
- After the air enters the outlets, and the pressure in them changes to the desired values, check the device for leaks, as it must have this quality in any position of the lever. Air leakage must not exceed 8 cm/min.
Agree, the procedure for replacing and disassembling the KamAZ brake valve cannot be called an easy task, which is why many motorists do not dare to deal with it. Perhaps this is the right decision, because if you are not a specialist, but only a driver who is not sufficiently versed in the design features of KamAZ trucks, then it would be better to entrust the matter to professionals.
Subscribe to our feeds on social networks such as Facebook, Vkontakte, Instagram, Pinterest, Yandex Zen, Twitter and Telegram: all the most interesting automotive events are collected in one place.
Did you know? The Kama Automobile Plant has been successfully operating since 1976, producing today not only diesel trucks, but also buses, tractors and combines.
Important! The slightest ingress of dirt on the lever system and rubbing surfaces can disable the crane.
Interesting! The first KamAZ-5320 vehicle left the main assembly line on February 16, 1976.
Air system KAMAZ 5511 | KAMAZ
Brake system KAMAZ
Pneumatic brake system
How to remove the main brake valve on a Kamaz 5511 car
Air leakage from the brake valve KAMAZ ZIL PAZ MAZ KRAZ GAZ
Brake systems KAMAZ
Why is KamAZ slowly getting on the handbrake
Brake valve handbrake KAMAZ
We put the KAMAZ accelerator on Foton 1093
Brake adjustment KAMAZ
I collect Kamaz for myself. Front brakes. (way out)
See also:
- KAMAZ in puddles video
- About long KAMAZ trucks
- KAMAZ tachometer connection diagram
- KAMAZ cars video for boys
- KAMAZ does not keep the temperature
- KAMAZ new video
- Clutch housing KAMAZ 4308
- Bad braking KAMAZ
- How many tons does a KAMAZ dump truck hold?
- Tire pressure KAMAZ 5320
- Side visors KAMAZ
- KAMAZ 65115 does not turn the starter
- KAMAZ trucks of the world video
- Driving of KAMAZ vehicles
- Tightening torque for KAMAZ 5320 heads
Home » New » Air system KAMAZ 5511 kamaz136.ru
Pneumatic drive KAMAZ
Pneumatic brake drive. The pneumatic brake actuator has a source of compressed air - compressor 1. Compressor, pressure regulator 2, fuse 3 from freezing condensate in compressed air and a condensate receiver
11 - the supply part of the drive, from which the purified compressed air under a given pressure is supplied to the rest of the pneumatic drive and to other consumers of compressed air. The drive is divided into autonomous circuits separated by protective valves. Each circuit operates independently of the others.
|
Fig.1. Pneumatic brake mechanism of the car KAMAZ-5320
The circuit I of the drive of the mechanisms of the service brake of the front axle consists of a part of a triple safety valve 5, a receiver 14 with a volume of 20 l with a condensate drain valve and a switch for the control lamp of pressure drop in the receiver, a part of a two-pointer pressure gauge 20, a lower section of a two-section brake valve 16, valve C of the control output , pressure limiting valve 18, two brake chambers 19, front axle brakes, pipelines and hoses between these devices.
In addition, the circuit includes a pipeline connecting the lower section of the brake valve 16 with the valve 26 for controlling the brake systems of the trailer with a two-wire drive.
Circuit II of the drive of the rear bogie service brake mechanism consists of a part of a triple safety valve, two receivers 12 with a total volume of 40 liters with condensate drain valves 15 and a switch for the pressure drop indicator lamp in the receiver, part of a two-pointer pressure gauge 20, the upper section of a two-section brake valve 16, valve D control output, automatic brake force regulator 25 with an elastic element, four brake chambers 21, brake mechanisms. The circuit also includes a pipeline connecting the upper section of the brake valve 16 with the valve 26 for controlling the brake systems of the trailer.
Circuit III of the drive mechanisms of the spare and parking brakes, as well as the combined drive of the brake systems of the trailer (semi-trailer) consists of a part of a double safety valve 4, two receivers 13 with a total volume of 40 l with a condensate drain valve and a switch for the warning lamp for pressure drop in the receiver, two valves E and B control outputs, a parking brake control valve 9, an accelerating valve 24, a part of a two-way bypass valve 23, four spring-loaded energy accumulators 21, a switch 22 for a parking brake warning lamp, a trailer brake control valve 26 with a two-wire drive, a single safety valve 27, a valve 29 control of trailer brake systems with a single-wire drive, three uncoupling valves 28, three connecting heads (one head 32 type A of a single-wire drive of trailer brake systems and two heads 31 of the Palm type of a two-wire drive of trailer brake systems), a pneumoelectric switch 30 of a brake signal, pipelines and hoses between these devices.
The circuit IV of the drive of the auxiliary brake mechanisms and other consumers consists of a part of a double protective valve 4, a pneumatic valve 8, two cylinders 7 of the damper drive, a pneumatic cylinder 6 of the drive of the engine stop lever, a pneumoelectric switch 17 of the trailer solenoid valve, pipelines and hoses between these devices. Circuit IV does not have its own receiver and pressure drop warning lamp. From circuit IV of the auxiliary brake mechanism drive, compressed air is supplied to additional consumers via a pneumatic signal, pneumatic clutch booster, transmission unit drives, etc.
| Rice. 2 |
Scheme of the pneumatic actuator KAMAZ-53212
Moisture-oil separator
| Rice. 3 |
When describing the components and the principle of operation, the pneumatic drive of the KAMAZ-5320 car was taken as the basis. However, you should be aware that the brake actuators of other cars have their own distinctive features. To improve moisture separation in the supply part of the brake drive of the KamAZ-53212 vehicle, a dehumidifier is additionally installed on the first cross member of the frame in the zone of intensive airflow at the compressor-pressure regulator section. The KamAZ-5511 dump truck does not have trailer brake control equipment, disconnecting valves, and coupling heads.
| Rice. 4 |
In addition, for KamAZ-5410, -5511 and 54112 vehicles, the safety valve block consists of a triple safety valve through which circuits I and II are filled with compressed air and a single safety valve through which circuit III is filled, and circuit IV is filled from circuit I or II.
autoruk.ru