Almost any modern car (except electric cars) is necessarily equipped with a gearbox. The most popular are the following types of gearboxes:
- Manual Transmission;
- Automatic transmission;
- Variable speed drive;
- Robotic gearbox.
The most common in Russia is a manual transmission. Almost all domestic cars and most foreign cars are equipped with boxes of this type.
Purpose and device of a manual transmission
A manual gearbox is needed in a car to change the gear ratio from the engine to the wheels. Gear shifting occurs due to the muscular strength of the driver, his mechanical efforts in relation to the manual transmission. That is why such a gearbox is called a manual gearbox. The driver himself controls when to shift the manual transmission selector to a higher or lower gear. Modern manual transmissions are 5, 6 and even 7-speed. Most often in modern cars a 6-speed gearbox is used.
In addition, each manual transmission box has a reverse and neutral gear. The rear one allows the car to move backward, the neutral gear is when there is no rotation from the motor to the drive of the drive wheels.
Why do you need a manual transmission?
The first reason is clear - you need to somehow connect the rotating shaft of the engine to the wheel drives in order to move off. There is a second: the power unit develops working power (otherwise - maximum torque) when a certain number of revolutions of the crankshaft is reached. For most gasoline engines, this threshold is 3000 rpm, for diesel engines it is 2000 rpm.
Until the number of revolutions of the crankshaft reaches the lower threshold, the motor will not be able to develop the necessary power and create enough force to move.
For dummies, that is, beginners who want to understand the operation of automotive components, the following explanation is offered:
- During on-site operation (idling), the number of revolutions of the crankshaft is 800-900 rpm. To start moving, the developed power is not enough and you need to raise it by pressing the gas and increasing the speed to 2-3 thousand per minute. At this point, you need to connect the wheel drive, which is done using the gearbox.
- Without a manual transmission, the acceleration of the car will be smooth and incredibly long, and if there is a rise, the car will never accelerate. The reason is the same - lack of power. To increase the dynamics, you need a force converter that can slow down the rotation, but increase the torque.
- For turning and parking, the car needs reverse gear, which is also provided by a manual transmission.
If a gear with gears of different sizes is placed between the wheel drive and the crankshaft, the wheels will rotate more slowly. But at the same time, the effort (in jargon - traction) will increase on each wheel and the acceleration of the car will accelerate. A smooth connection of rotating elements will provide another manual transmission unit - the clutch.
The principle of operation of a manual transmission
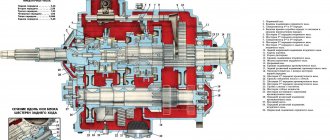
The manual transmission device includes:
- The box itself, which is a multi-stage gearbox;
- Clutch;
- Various shafts and gears.
If you explain the principle of operation of manual transmission for dummies, then you can form it like this:
- The gears change the speed between the shafts. By changing the size of the gears, there is a switch to an up or down gear;
- Without a clutch, shifting gears on the go is impossible. His job is to separate the motor and transmission. This procedure helps to shift gears without breaking the gears and shaft.
Each manual transmission (if it is not an innovative model) is arranged according to a similar design. Gears are located on the shafts (on their axes). Manual transmissions come with two or three shafts, and the housing is called the crankcase.
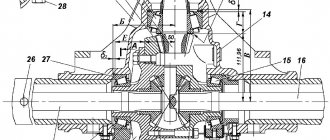
Synchronizers
It is an important component of any mechanical transmission. Synchronizers serve to smooth the speed of rotation of the gear and shaft. Gear shifting thanks to synchronizers is quick and smooth. The device includes:
- Blocking ring.
- Hub.
- A gear with a friction cone.
- Clutch of inclusion.
The hub is the main element of the node. It has two slots (external and internal). Due to them, the mechanism is connected to the transmission shaft, moving along it in different directions. Thanks to the outer slot, the element is connected to the clutch. Also, the hub device assumes the presence of three grooves. Each is set at an angle of 1200 relative to each other. These grooves are used to install "crackers". What it is? These are spring-loaded elements that fix the clutch in the "neutral" position. With this installation of the clutch, the box synchronizer does not work. The flywheel rotates freely without transmitting torque to the box. The clutch itself connects the gears to the box shaft. The part is mounted on the hub. From the outside, it connects to the gearbox fork.
Image taken from carnovato.ru
To equalize the angular velocities, a blocking ring is used . The smoothing of rotation occurs due to friction. The ring prevents the clutch from closing until the gear and shaft have equal rotational speeds. The inner part of the blocking ring has a conical shape.
How does a synchronizer work in a manual transmission:
- The clutch is in the middle position when not in use. The gears on the transmission shafts rotate freely.
- When the driver selects a gear, the clutch moves to the gear through the fork. In this case, the clutch moves the blocking ring. The latter is pressed against the gear cone.
- The ring rotates and blocks the subsequent movement of the clutch.
- Due to friction, the revolutions of the shaft and gear are aligned.
- The clutch engages the shaft and the gearbox gear.
- Torque is transmitted from the engine flywheel.
Three-shaft system device
The three-shaft system is equipped with three shafts:
- drive shaft;
- intermediate shaft;
- Driven shaft.
The principle of operation of the mechanics is that there are splines on the drive shaft, and the shaft itself is connected to the clutch. The clutch disc moves on the splines, and the axle itself transfers its energy to the intermediate shaft, which is connected to the drive gear.
The driven shaft of a mechanical gearbox is connected to the drive shaft with the help of a bearing inside the first shaft and is located in such a way that the axes of the driven and the drive are related to each other. In turn, this structure allows them to rotate independently of each other. The gears of the driven axle are not rigidly fixed in relation to the driven shaft, and the gears themselves have special delimiters - a synchronizer clutch. Such delimiters, unlike gear blocks, are firmly attached to the driven shaft. However, this does not prevent them from moving along the spitz along the axis.
The ends of the synchronizer coupling are in the form of gear rims, which allows them to come into contact with the rims on the ends of the driven shaft gears. Currently, the gear unit is equipped with such synchronizers in all forward gears.
Delimiters-couplings in the neutral mode, which is characterized by smooth rotation of the gears, are disengaged. At the moment of switching the lever to one of the possible steps with the clutch fully depressed, the fork in the gearbox directs the synchronizer clutch to come into contact with its pair at the end of the gear. This engagement gives a rigid fixation of the gear with the shaft and, as a result, the transmission of force and rotation.
With a rear-wheel drive type of car, the transmission of torque and revolutions to the drive wheels occurs through a cardan shaft, and with a front-wheel drive - using CV joints and a gearbox. In the event that there is no gear, and the clutch directly engages the driven and drive shafts, the gearbox gives the highest possible efficiency. For reverse gear, the box device is equipped with a gear that allows you to change the direction of rotation in the reverse order.
Recently, manual transmission manufacturers have been favoring helical gears. Unlike spur gears, such gears produce a minimum of noise during operation and are more wear resistant. The service life of such gears is determined by the material from which they are made: high-alloy steel, hardened by high frequency current and normalized to relieve stress.
Gearboxes with design specifics
In addition to well-known transmissions, unique modifications can also be used in vehicles. These types of boxes have a specific design, and with it their own principle of operation.
Shaftless gearbox
Transmissions that do not use shafts with a set of gears are called shaftless. In their design, they have several rows of gears located in two parallel axes. The gears are connected by locking the clutches.
Gears are located on two shafts. Two of them are fixed tightly: on the leader it is installed in the first row, and on the slave - in the last. The intermediate gears located on them can play the role of a master or a slave, depending on the generated gear ratio.
This modification allows you to increase the gear ratio in both directions. Another advantage of such a transmission is the increased power range of the box. One of the most serious drawbacks is the mandatory presence of an auxiliary automatic system with which the gears are switched.
Unsynchronized gearbox
Another type of specific boxes is non-synchronized or one that does not provide for the presence of synchronizers in the design. It can be a constant mesh type or a sliding gear type.
To change gear in such a box, the driver must have a certain skill. He must be able to independently synchronize the rotation of gears and clutches, determining the transition time from gear to gear, as well as equalizing the speed of rotation of the crankshaft with an accelerator. Professionals call this procedure regassing or double clutch release.
To perform smooth shifting, the driver must be experienced in operating such mechanisms. A similar type of transmission is installed in American tractors, motorcycles, sometimes in tractors and sports cars. In modern non-synchronized transmissions, it is possible not to use the clutch.
Cam gearbox
Cam boxes are a kind of non-synchronized model. The difference is the shape of the engaged teeth. To increase the efficiency of the gearbox, a rectangular shape or cam tooth profile is used.
Such boxes are very noisy, therefore, in passenger vehicles they are used mainly on racing cars. During the competition, this factor is not paid attention, but in a conventional car, such a transmission will not make it possible to enjoy the ride.
Sequential CP
A sequential gearbox is a type of transmission in which the downshift or upshift is carried out exclusively by one step. For this, a handle or foot switch (on motorcycles) is used, which allows you to move the gear in the basket only one position at a time.
A Tiptronic type automatic transmission has a similar principle of operation, but it only imitates the action of this transmission. The classic sequential box is installed in F-1 cars. Switching speed in them is carried out with the help of steering-wheel paddles.
Preselective CP
In the classic version, the preselective gearbox required a preliminary selection of the next gear before the box switched to it. It often looked like this. While the car was moving, the driver put the next gear on the selector. The mechanism was preparing to switch, but did it on command, for example, after pressing the clutch.