Adjustment of gaps and bearings of the drive axle UAZ-3741, UAZ-3962, UAZ-3909, UAZ-2206, UAZ-3303
Adjustment of the gaps in the gear engagement and in the bearings of the drive axle of cars of the wagon layout UAZ-3741, UAZ-3962, UAZ-3909, UAZ-2206, UAZ-3303 is carried out only when replacing gears or bearings, or when an axial clearance of the driving or driven gears of the main transmission. The replacement of the gears of the main gear must be carried out only as a complete set.
Adjustment of the bearing of the main gear of the main drive of the drive axle UAZ-3741, UAZ-3962, UAZ-3909, UAZ-2206, UAZ-3303
Adjustment of the bearing of the drive gear of the main gear of the drive axle must be carried out by selecting the thickness of the package of shims and tightening the flange nut. The bearing must have such a preload that there is no axial movement of the drive gear, and the gear is rotated by hand without much effort.
Check the bearing preload with a dynamometer. In doing so, disconnect the left half of the crankcase.
Remove the pinion bearing cap so that the cuff friction does not affect the dynamometer reading.
With proper adjustment, at the moment of turning the drive gear through the hole in the flange, the dynamometer should show a force of 1.5-3 kgf for worn-in bearings and 2.0-3.5 kgf for new bearings.
When replacing the cover, align the oil holes in the crankcase, gasket and cover. The tightening torque of the pinion flange mounting nut should be 17-21 kgcm.
You can not even unscrew the nut a little in order to match the cotter pin hole with the nut slot.
If the nut is not tightened enough, the inner rings of the bearing may rotate and, as a result, wear of the adjusting shims and the appearance of a dangerous axial clearance.
If axial clearance of the drive gear appears during operation of the vehicle, tighten the flange nut. If this does not eliminate the axial clearance, then reduce the thickness of the shim pack and adjust the bearing as indicated above.
After adjustment, monitor the heating of the bearings during movement. A slight heating of the bearing is not dangerous, but if the neck of the drive axle housing heats up to a temperature of 90 degrees and above, the water boils on the crankcase, this means that the bearing has been overtightened and the total thickness of the gaskets should be increased.
Adjustment of the differential bearings of the drive axle UAZ-3741, UAZ-3962, UAZ-3909, UAZ-2206, UAZ-3303
The differential bearings must be adjusted by selecting the thickness of the package of shims installed between the ends of the inner rings of both bearings and the satellite box. When replacing the final drive gears and differential bearings, adjust in the following sequence:
1. Press the inner rings of the differential bearings onto the necks of the assembled differential so that there is a gap of 3-3.5 mm between the ends of the satellite box and the ends of the inner rings of the bearings.
2.
Remove the axle shafts and install the differential assembly with the driven gear in the crankcase, put the gasket and cover, screw on the cover fastening bolts and turning the driven gear with a mounting blade through the crankcase neck, roll on the bearings so that the rollers take the correct position. Then fasteners evenly and finally connect the cover to the crankcase.
3. Unscrew the fasteners again. Carefully remove the cover, remove the differential from the axle housing and use a feeler gauge to measure the gaps A and A1 between the ends of the satellite box and the ends of the inner bearing rings.
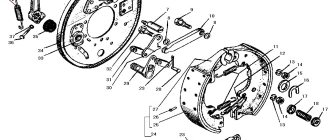
Adjustment of final drive bearings UAZ Patriot
Axial clearance in the bearings of the drive gear of the final drive is not allowed, because if it is present, the gear teeth wear out quickly and the bridge may jam.
Check the presence of axial clearance by rocking the drive gear by the flange of the cardan shaft.
To eliminate the axial clearance of the drive gear, it is necessary to tighten the nut 8 (Figure 1).
At the same time, keep in mind that the nut has a punching into the groove of the threaded part of the drive gear and when tightening, more force on the key will be required.
Tighten the nut carefully until the axial clearance of the drive gear is eliminated, avoiding its tightening, then tighten the nut.
If it is not possible to tighten the centered nut, then it should first be loosened by 0.5 - 1.0 turns, and then tightened until the axial clearance is eliminated and tightened.
Axial play in the bearings of the final drive differential is also not allowed.
Check it by rocking the driven gear 2 with the cover 21 of the crankcase removed.
Remove the axial clearance of the driven gear of the final drive by tightening the nut 17 of the differential bearing, having previously removed the locking plate 19.
Adjust bearings of the main transfer in a following order.
1. Pick up the adjusting ring 5 (see Fig. 1). Its thickness d1 (Fig. 2) is determined (with an accuracy of ±0.025 mm) based on the actual dimensions B and D (see Fig. 2 and 3) according to the formula d1 = B - (111.960 + D) (mm) .
Install the ring in the crankcase 16 (see Fig. 1) of the final drive.
2. Install the drive gear shaft into the front axle housing.
Check the torque of the drive gear shaft. It should be 1.0–2.0 N cm (0.1–0.2 kgf cm).
3. When installing the differential assembly with the driven gear, measure the dimension E (Fig. 4), applying an axial force P equal to 4000–5000 N (400–500 kgf) and turning the gear several times so that the bearing rollers take the correct position.
Measure the distance B in the crankcase (see Fig. 2) from the axis of the drive gear to the thrust end of the differential bearing.
According to the actual dimensions B, E and the mounting size of the driven gear, equal to 50 mm, select (with an accuracy of ± 0.025 mm) the adjusting ring according to the formula d2 = B - (E + 50 + X) (mm), where d2 is the thickness of the adjusting ring; X - the maximum deviation from the mounting size, equal to 50 mm, with the appropriate sign (plus or minus), this size is applied by electrograph to the end of the driven gear.
4. Install the differential assembly with the outer rings of its bearings and the adjusting ring in the front axle housing and secure it.
5. Adjust the bearings 6 and 22 (see Fig. 1) of the front axle differential by tightening the nut 23, periodically rotating the differential so that the bearing rollers are in the correct position. After tightening the nut, the total turning torque of the differential drive gear (Mv. sh.) Should be within Mv. sh. + (0.21–0.42) (Nm) . Check by turning the drive gear.
Check and adjust the side clearance in the engagement of the gears of the installed new final drive kit after adjusting the position of the gears.
The side clearance is checked with an indicator, the stand of which is attached to the axle housing in the direction perpendicular to the surface of the driven gear tooth when the indicator stand is attached to the housing of the indicator stand.
Check the gap on three or four teeth evenly spaced around the circumference.
The spread of gap values should not exceed 0.05 mm.
Normal side clearance should be between 0.15–0.25 mm.
If the backlash is less than the specified value, then the selected adjusting ring should be replaced with a ring of smaller thickness.
When checking and adjusting the side clearance, it is not necessary to create a preload in the differential bearings.
6. Tighten the adjusting nut 23 until it comes into contact with the bearings and there is no play in them.
7. Check the engagement of the main gear gears along the contact patch, for which paint the teeth of the driven gear with paint (2 teeth in three to four places evenly around the circumference).
8. Slowing down the drive gear shaft by the flange, rotate the driven gear in both directions until contact spots appear on the gear teeth, as shown in fig. 5
With the correct adjustment of the meshing of the gears, the contact patch should be located in the places of the teeth shown in the figure (pos. 1)
With contact at the top of the tooth (key 2), move the drive gear towards the driven gear by increasing the thickness of the adjusting ring, and move the driven gear away from the drive gear to maintain backlash.
With contact at the base of the tooth (key 3), move the drive gear away from the driven gear by reducing the thickness of the adjusting ring, and move the driven gear towards the drive gear to maintain backlash.
With contact at the narrow end of the tooth (key 4), move the driven gear away from the drive gear by reducing the thickness of the adjusting ring, while moving the drive gear towards the driven gear to maintain backlash.
With contact at the wide end of the tooth (key 5), move the driven gear towards the drive gear by increasing the thickness of the adjusting ring, and move the drive gear away from the driven gear to maintain backlash.
Install the lock plate on the differential bearing cap.
After assembling the main gear, check its heating after making a test drive in the car.
If the front axle housing in the area of the pinion bearings and differential bearings heats up above 90°C, adjust the bearing preload again as described above.
Rear axle device UAZ 469
Device of this node
The Soviet SUV UAZ 469, produced by the Ulyanovsk Automobile Plant, is unique in its own way. The diagram of the rear axle of the machine is shown in fig. 1. The design includes the following key components and assemblies:
- 1 - protective cover;
- 2 - roller bearing of the differential device;
- 3, 8 - corrective automatic pads;
- 4 - tail part of the drive gear support;
- 5 - correction ring;
- 6 - oil extractor holder;
- 7 - nut;
- 9 - front gear of the rear axle;
- 10 - head bearing support;
- 11 - hydro-resistant washer of the axle shaft of the gear wheel;
- 12 - gear element.
The device and elimination of breakdowns of the rear axle
The rear axle is a support, inside it is the main gear of the axle shaft, the differential. It can be of two categories: with a single final drive or an additional wheel drive. Wheel regulators, which increase the torque and transmit it to the hubs of the conductive wheels, are located at the ends of the beam.
Nuances of installation and adjustment
The assembly (diagram) of the differential drive design is carried out as follows.
- Connection of both boxes of satellites depending on the case serial number.
- A crosspiece is inserted into the left box of satellites.
- Place the assembly gear in the left box.
- Lubricate the differential units with gear oil (gear axles, pinion gears, axles, thrust washers).
- Fix the necks of the gear rings of the semi-axes with support washers.
- Satellites must be strengthened on the axis of the disconnected cross.
- Carry out the same actions with the right box.
- Tighten the parts of the boxes, insert the driven wheel of the base gear.
The master sorts out the unit
Turn the gears of the axle shafts of the mounted differential using splines with a force of not more than 59 N. Adjustment of the drive structural elements is carried out when replacing them.
- Fasten the inner rings of the bearing assemblies of the differential to the necks, the end play between the box and the rings should approach a value of 3.5-4.0 mm.
- The installed prefabricated differential is closed with an auto gasket, a reservoir cap. Roll on the bearings to set the correct position. Fasten the lock of the heat exchanger.
Mounting and adjustment of the ball bearings of the conductive gear of the rear converter.
- Fixing the elements of the guide on the main gear.
- Tail end lapping with guide element.
- Location of spacers and spacers of the roller assembly between the inner races.
- The main fastener of the adjusting ring of the main gear.
All intermediate actions, punching is shown by the diagram in fig. 2. This scheme describes all the nuances in the most detail.
- When adjusting the head gear assembly, there should be no longitudinal play, the spring dynamometer will show the force. Indicators for new parts - 15-30 N, for run-in - 20-35 N. To reduce the tension when installing bearings, you can add gaskets. To increase - remove.
- The adjustment has come to an end, we fix all the parts in their places, we fasten them with high quality.
The backlash adjustment and the location of the central gear gear are carried out as follows.
- The potential is installed in the heat exchanger with debugged prefabricated roller bearings, their separation gasket with a cover reinforced with a bolt.
- The distance between both teeth is set: 0.2-0.6 mm. The backlash is adjusted by taking into account the number of oil seals of the driven gear: if their number decreases, the gap must be increased, and vice versa. When rearranging the gaskets, the tightness of the potential elements will not be violated only when the number of gaskets does not change.
- The scheme of engagement of gear wheels along the contact patch is shown in fig. 3.
Features of dismantling the assembly
When removing the rear axle, you need to unscrew the nut of the tail device, drop the washer, counterflange, cover of the front roller gear assembly, press the gear assembly with bearings out of the oil cooler of the rear of the car.
This circuit is great for parsing a differential device. The next step is to unscrew the splines connecting the driven gear to the satellite box, reset it. Divide both parts of the box, pull out the gears, planetary wheel rods, support nuts. Assessing the disassembly, pay attention to the integrity of the gear teeth. If they are damaged, the part must be replaced. To remove the rollers, outer, inner rings, special tools are required. Strictly study and understand the disassembly sequence so that you can accurately follow all the steps in reverse order when reassembling.
When inspecting the oil ring, check for surface irregularities. If yes, process to a thickness of 5 mm. The same is with the cardan flange. Grinding height up to 53 mm. Rinse protective surfaces. Blow out oil lines. Change drive design details, half shafts, if there are scuffs, severe wear.
Bridges UAZ
Many variants of bridges were installed on UAZ cars of different models and at different times at the plant. Let's try to figure this out...
Bridge UAZ Timken (civilian or collective farm)
This is a split type bridge, that is, a bridge consisting of two halves. A military bridge (it is also a gear or portal bridge) can also be attributed to the same type. From the factory, civilian bridges are installed on UAZ cars of the cargo range (loaf, onboard, farmer), as well as on cars of the UAZ-3151 (469) passenger car series.
Front civil Timken bridge for UAZ 469 cars and a loaf
Rear axle Timken (civilian), for cars UAZ 469 and loaf
Photo of a gearbox of a half-witted civil bridge
Photo of Timken civil bridge shank
The so-called hybrid bridges are installed on the UAZ Hunter, with a stocking from conventional Timken bridges and a steering knuckle from Spicer.
Gear ratios of the Timken bridge (civil).
Until July 1989, the main pair with a gear ratio of 5.125 (41 teeth) was installed in civilian bridges, now with a gear ratio of 4.625 (37 teeth), i.e., more “fast”, but less “powerful”. You can find both in stores. Most likely, you will have to replace the “new” with the “old” main pair when installing very large wheels. It is recommended to replace the main pairs only as a complete set (in the front and rear axles), otherwise the front axle will have to be turned on exclusively in mud, snow, sand, etc., so as not to damage the transfer case and ruin the rubber. How to determine the gear ratio? It is necessary to twist the cardan with your hands and count the revolutions of the wheel. For example, 46 revolutions of the cardan - 10 wheels = a pair of 4.6, etc.
Main pair for UAZ, Timken bridges, hybrid, 37-8, 4.625
Weight of civil bridges UAZ:
- front axle - 132 kg
- rear axle - 100 kg
UAZ gear (military) axles
In fact, this is the Timken Bridge, i.e. split, but it has a smaller central gearbox and final drives. The plant installed military bridges on UAZ 469 vehicles for the army and UAZ, Bars. UAZ Bars bridges are military bridges, but with a wider gauge.
UAZ military bridges
Photo of UAZ military bridges
Photo final drive UAZ
Photo rear military bridge UAZ
Portal bridges UAZ Bars
Bridges UAZ Bars installed on UAZ Loaf
Gear ratios of UAZ military bridges
The gear ratio of military bridges is 5.38 (= 2.77 * 1.94 - gear ratios, respectively, of the main and final drives) - more high-torque, but less speedy than conventional bridges.
Characteristics of the military bridge
- Ground clearance: 300 mm (with tires Ya-192 215/90 R15 (31 x 8.5 R15)
- Track: 1445 mm
- Track gear axles UAZ Bars: 1600 mm
- Weight of UAZ military front axle: 140 kg
- UAZ military rear axle weight: 122 kg
Scheme of the gear (military) bridge UAZ
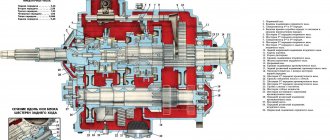
Rear axle UAZ with final drive:
1 – a cover of a crankcase of the main transfer; 2 - differential bearing; 3,13,49 - shims; 4 - sealing gasket; 5.7 - bearings of the drive gear; 6.15 - adjusting rings; 8.42 - cuffs; 9 - flange; 10 - nut; 11 - mud deflector; 12 - ring; 14 - spacer sleeve; 16 - main gear drive; 17 - satellite; 18 - right axle shaft; 19 – final drive housing; 20.29 - oil deflectors; 21 - axle bearing; 22,26,40 - retaining rings; 23 - sealing gasket of the final drive housing; 24 – final drive housing cover; 25 - bearing; 27 - brake shield; 28 - brake drum; 30 – a bolt of fastening of a wheel; 31 - trunnion; 32 - hub bearing; 33.41 - gaskets; 34 - lock washer; 35 - leading flange; 36 – a nut of bearings of a nave; 37 - lock washer; 38 - bushing; 39 - driven shaft final drive; 43 - driven shaft bearing; 44 - driven gear final drive; 45 - special nut; 46.50 - drain plugs; 47 - final drive gear; 48 - right cup of the box of satellites; 51 - main gear housing; 52 – half shaft gear washer; 53 - half shaft gear; 54 - the axis of the satellites; 55 - driven gear of the main gear; 56 - left cup of the satellite box; 57 - left half shaft
Scheme of the rear military bridge UAZ
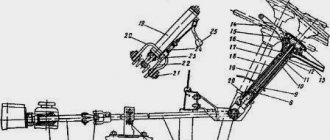
UAZ front axle steering knuckle with final drive:
a - signal groove; I - right rotary fist; II - left rotary fist; III - wheel disconnect clutch (option see Fig. 180, IV); 1 - stuffing box; 2 - ball bearing; 3 – the hinge of a rotary fist; 4 - gasket; 5 - press grease fitting; 6 - kingpin; 7 - overlay; 8 - body of the steering knuckle; 9 - kingpin bushing; 10 - bearing; 11 - driven shaft of the final drive; 12 - hub; 13 - leading flange; 14 - clutch; 15 – lock ball; 16 - protective cap; 17 - coupling bolt; 18 - trunnion; 19 - lock nut; 20.23 - support washers; 21 - final drive gear; 22 - locking pin; 24 - rubber sealing ring; 25 - thrust washer; 26 - axle housing; 27 – a bolt of restriction of turn; 28 - emphasis-limiter of rotation of the wheel; 29 - steering knuckle lever
Scheme of the steering knuckle of the front military axle with final drive
The device and elimination of breakdowns of the rear axle
The rear axle is a support, inside it is the main gear of the axle shaft, the differential. It can be of two categories: with a single final drive or an additional wheel. Wheel regulators, which increase the torque and transmit it to the hubs of the conductive wheels, are located at the ends of the beam.
The wheel roller bearings are supported by the governor housings. Wheel reduction gears provide huge ground clearance and are gears meshed inside. The main gear is bevel, with a spiral tooth, bearing assembly, which has a main gear and a conical drive with 4 satellites. The satellite is a gear wheel, compact, simple, rarely fails, contributes to quick, easy gear changes.
The crankcase has a drain and filler hole, it contains a certain amount of oil for lubricating the wheel hydraulic regulator.
The rear transducer support is detachable and consists of elements such as a cover, protection against contamination, pressed-in axle shaft covers. Its dimensions are reduced, the gear ratio is up to 2.77.
The driven rear axle reducer is mounted on the shaft. It is installed in a roller bearing and bushing, tightened by means of a nut, fixed in the groove of the shaft. The ends of the gearbox shafts have movable couplings that help to group, separate the shafts from the wheel hubs, if necessary.
With the clutches disconnected, the UAZ 469 becomes rear-wheel drive. This is useful on good paved roads. When driving on impassable terrain, disabling is impractical. You can disconnect-connect the hubs from the beginning of the operation of the quick response clutch or the hub cam. In this case, climbing under the bottom of the car is not required.